1、sort()方法
列表中所有元素默认从小到大的顺序进行排序(升序),可以通过设置参数 reverse=True 进行降序排序。无返回值。
语法格式:list_name.sort(reverse = True|False, key = Function)
参数说明:
reverse:可选参数。reverse 的默认值是False,表示升序,reverse = True 时,表示降序。
key:可选参数。指定排序标准的函数。只有一个参数,具体的函数的参数就是取自于可迭代对象中,指定可迭代对象中的一个元素进行排序。
返回值:无返回值。
代码演示:
1)无参
不设置任何参数的话,默认是升序排序。
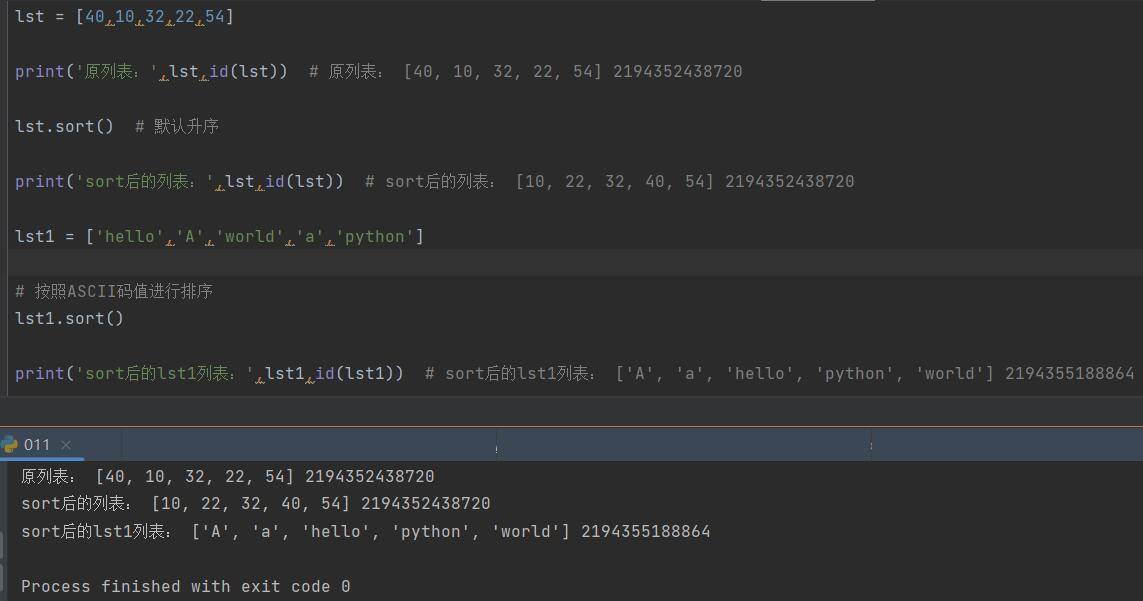
lst = [40,10,32,22,54]
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) # 原列表: [40, 10, 32, 22, 54] 2194352438720
lst.sort() # 默认升序
print('sort后的列表:',lst,id(lst)) # sort后的列表: [10, 22, 32, 40, 54] 2194352438720
lst1 = ['hello','A','world','a','python']
# 按照ASCII码值进行排序
lst1.sort()
print('sort后的lst1列表:',lst1,id(lst1)) # sort后的lst1列表: ['A', 'a', 'hello', 'python', 'world'] 2194355188864![图片[1]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/9926f78039170721.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
2)通过设置参数 reverse=True 进行降序排序。
reverse 默认为False。
lst = [40,10,32,22,54]
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) # 原列表: [40, 10, 32, 22, 54] 2887170522560
# 通过设置参数进行降序排序
lst.sort(reverse=True)
print('sort(reverse=True)后的列表:',lst,id(lst)) # sort(reverse=True)后的列表: [54, 40, 32, 22, 10] 2887170522560![图片[2]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/d9ce712cb8171433.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
如果列表中的元素无法直接比较大小,就必须指定key参数。
3)设置key参数来指定排序标准
通过设置 key 参数来指定排序标准的函数。这个函数只有一个参数,具体的函数的参数就是取自于可迭代对象中,指定可迭代对象中的一个元素进行排序。
返回列表中由于计较大小的元素。
代码演示:根据列表元素的长度来进行排序。
lst = ['hello','999','word',10,'python']
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) #
def myFun(x):
return len(str(x)) # 如果是整型,则无法使用len计算长度,所以要使用str()进行类型转换
# 根据字符串的长度进行排序,将lst列表中的数据先传入len()函数中计算字符串长度,再作比较。
lst.sort(key = myFun)
print('列表:',lst,id(lst))![图片[3]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/c037b7c98f175422.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
使用lambda表达式:
lst = ['hello','999','word',10,'python']
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) #
# 根据字符串的长度进行排序,将lst列表中的数据先传入len()函数中计算字符串长度,再作比较。
lst.sort(key = lambda x: len(str(x)))
print('列表:',lst,id(lst))a、列表中既有整型,也有字符串类型,无法直接比较大小,可以自定义函数或使用lambda表达式来处理数据。
如果列表中既有字符串类型,又有整型,直接排序会报错,因为字符串和整型无法比较大小。
lst = ['hello',999,'word',10,'python']
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) #
lst.sort()
print('列表:',lst,id(lst))![图片[4]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/18be880af7173207.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
可以通过设置 key 参数,对列表中的数据进行处理后再排序。
lst = ['hello',999,'word',10,'python']
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) #
def myFun(x):
return str(x) # 转换为str类型
# 比较之前,先将列表中的数据传递到myFun中进行处理
lst.sort(key = myFun)
# 等价于
# lst.sort(key = lambda x: str(x))
print('列表:',lst,id(lst))![图片[5]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/bf641cdfad173804.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
b、对元组组成的列表进行排序
元组之间无法直接进行比较大小,可以使用自定义函数来获取元组中的某个元素来代表元组进行大小比较。
lst = [(12,100),(4,8),(2,4),(9,32)]
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst))
def myFun(x):
return x[1] # 返回列表的第二个元素,元组是有序的,可以通过索引来访问元素
lst.sort(key = myFun) # 将列表的每一个元素传入myFun中
# 使用lambda表达式
# lst.sort(key = lambda x: x[1])
print('排序后:',lst,id(lst))![图片[6]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/65cc11187c180232.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
字典组成列表同理。
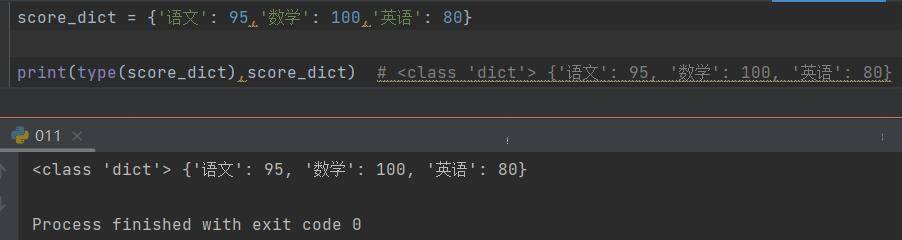
2、内置函数sorted()
默认升序,可以通过设置参数 reverse=True 进行降序排序。产生新的列表对象。
语法格式:new_list = sorted(iterable, key=myFun, reverse=True/False)
参数说明:
iterable:列表对象。可迭代对象
key:可选参数。指定排序标准的函数。只有一个参数,具体的函数的参数就是取自于可迭代对象中,指定可迭代对象中的一个元素进行排序。
reverse:可选参数。表示排序规则。reverse 的默认值是False,表示升序,reverse = True 时,表示降序。
返回值:返回排序后的新列表对象。
1)列表中的元素同为整型,或者同为字符串类型,可以直接比较大小
lst = [40,10,32,22,54]
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) # 原列表: [40, 10, 32, 22, 54] 2148274077120
# 默认升序
new_lst = sorted(lst)
print('排序后的列表',new_lst,id(new_lst)) # 排序后的列表 [10, 22, 32, 40, 54] 2148277154944
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) # 原列表: [40, 10, 32, 22, 54] 2148274077120![图片[7]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/cacc62c0d6202622.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
2)reverse参数
默认为False,表示升序。若reverse = True,则表示降序。
lst = [40,10,32,22,54]
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) # 原列表: [40, 10, 32, 22, 54] 2148274077120
# 默认升序
new_lst = sorted(lst,reverse=True)
print('排序后的列表',new_lst,id(new_lst)) # 排序后的列表 [10, 22, 32, 40, 54] 2148277154944
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) # 原列表: [40, 10, 32, 22, 54] 2148274077120![图片[8]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/1268affcde202822.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
3)若元素不可以直接比较大小,就要设置key参数
如字符串和整型,无法直接比较大小。要通过自定义函数或者 lambda 表达式进行处理。
lst = ['40',50,'hello',22,'A',0]
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) # 原列表: ['40', 50, 'hello', 22, 'A', 0] 1932366904768
# 字符串和整型无法直接比较大小,可以通过自定义函数或者lambda表达式处理
new_lst = sorted(lst,key = lambda x: str(x))
print('排序后的列表',new_lst,id(new_lst)) # 排序后的列表 [0, 22, '40', 50, 'A', 'hello'] 1932370178432
print('原列表:',lst,id(lst)) # 原列表: ['40', 50, 'hello', 22, 'A', 0] 1932366904768![图片[9]-Python列表的两种排序方式的比较(sort()和sorted())-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/c9682646c1203719.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
sort() 和 sorted() 的区别
sort():是list中的一个方法,在原列表中进行操作,不产生新的列表对象。无返回值。
sorted():是Python内置函数,可以直接使用,sorted对列表进行排序,会产生新的列表对象,原列表不发生改变。返回值是新的列表对象。
1 本站一切资源不代表本站立场,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责。
2 本站一律禁止以任何方式发布或转载任何违法的相关信息,访客发现请向站长举报。
3 本站资源大多存储在云盘,如发现链接失效,请联系我们我们会第一时间更新。




暂无评论内容